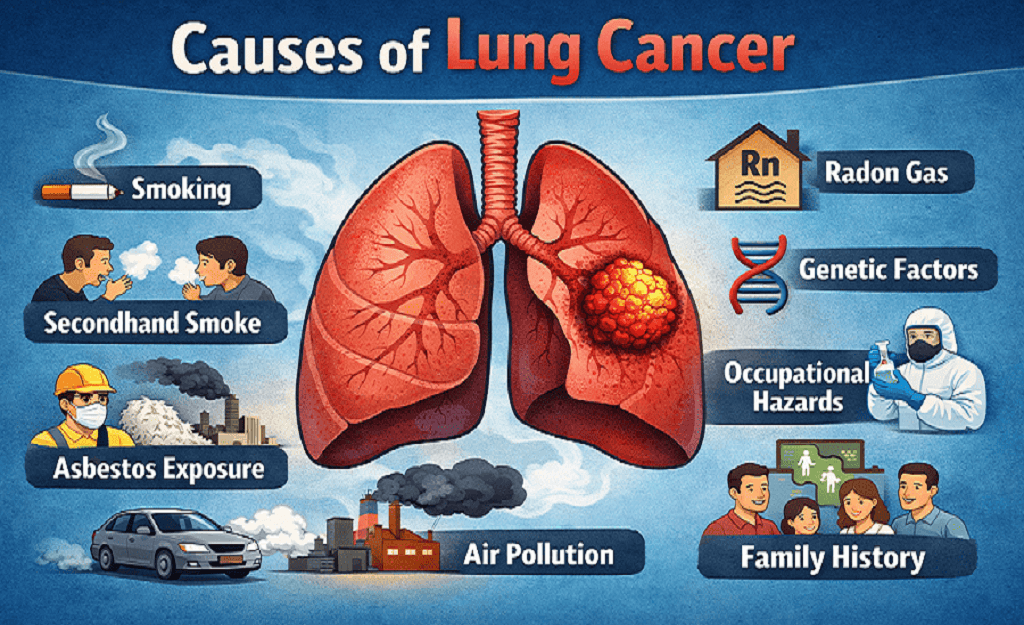
When most people think about lung cancer, smoking is usually the first cause that comes to mind. While it is true that smoking remains the leading cause of lung cancer, the full picture is much broader. Doctors today are seeing a steady rise in lung cancer in non-smokers, which makes it essential to understand the many causes and risk factors beyond tobacco.
This article explains the real causes of lung cancer, why people who have never smoked can still develop the disease, common warning signs, and how early diagnosis and the right treatment can improve outcomes—especially for patients seeking expert care in Kolkata.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer begins when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs. It is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide and accounts for a significant number of lung cancer deaths each year. According to the National Cancer Institute, lung cancer incidence remains high even as smoking prevalence declines, showing that smoking alone does not explain all cases.
Types of Lung Cancer
Doctors broadly classify the disease into two main types of lung cancer:
- Non-small cell lung cancer – the most common type,
- Small cell lung cancer – less common but most aggressive and often linked to long-term smoking.
Identifying the type is important because it directly affects prognosis and treatment planning.
What Really Causes Lung Cancer?
The development of lung cancer usually happens over time due to repeated damage to lung cells. This damage may come from toxins in the air, inherited changes, or long-term inflammation. These exposures can trigger genetic mutation, allowing abnormal cells to grow unchecked. In most patients, multiple causes and risk factors work together rather than a single trigger.
Smoking and Lung Cancer Risk
Smoking cigarettes significantly increases the risk of lung cancer. A regular smoker, particularly among heavy smokers, inhales thousands of toxic chemicals from cigarette smoke that damage lung tissue. Lung cancer remains strongly associated with smoking and is still the most common cancer caused by smoking.
The good news is that risk can be reduced. Quitting smoking lowers the risk of developing lung cancer over time and remains one of the most effective strategies for cancer prevention.
Non-Smoker Lung Cancer Causes
Lung cancer isn’t limited to people who smoke. Many patients diagnosed today have never smoked. In these cases, doctors often find links to environmental exposure, inherited risk, or chronic lung irritation. This explains why lung cancer is increasingly seen among individuals with no history of tobacco use.
Lung Cancer Risk Factors Other Than Smoking
Several well-established factors can increase lung cancer risk even in non-smokers:
- Air pollution: Chronic exposure to air pollution, especially outdoor air pollution in urban settings, has been linked to lung inflammation. Pollutants such as diesel exhaust can damage lung cells and increase the risk of developing cancer. As per World Health Organisation (WHO) the most important cause of lung cancer is air pollution
- Radon exposure: Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can build up indoors. Long-term exposure is known to increase lung cancer risk, even in people who have never used tobacco.
- Secondhand smoke: Regular exposure to secondhand tobacco fumes at home or work raises overall cancer risk. Long-term exposure can damage lung tissue in ways similar to direct smoking.
- Occupational hazards: Long-term exposure to substances like asbestos or asbestos fibers at work can seriously harm lung tissue. These exposures may lead to lung cancer decades later.
- Chronic lung disease: Ongoing inflammation from chronic lung conditions may gradually damage cells and raise the risk for lung cancer. Healed scar of tuberculosis often leads to adenocarcinoma of lung
Who are at Higher Risk?
People at higher risk include those with prolonged exposure to polluted air, individuals working in hazardous environments, and people with inherited genetic changes. Even people who have never smoked may develop lung cancer when multiple risk factors combine, which explains why lung cancer due to non-smoking causes is increasingly recognized.
Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
The symptoms of lung cancer can be mild or vague in the early stages and are often mistaken for common respiratory illnesses. Warning signs may include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
If any of the warning signs are there for more than 4 weeks, one should consult a doctor immediately. Because most patients ignore these symptoms, unfortunately many patients are diagnosed only when the disease is advanced.
Why Stage 4 Lung Cancer Can Occur in Non-Smokers
In non-smokers, advanced lung cancer is often linked to delayed diagnosis. Without obvious risk factors such as smoking, early symptoms may be overlooked. Environmental exposures, genetic mutations, and lack of routine screening can result in patients being diagnosed with lung cancer only after it has spread.
The Top Causes of Lung Cancer
From a clinical perspective, the most common causes include:
- Smoking
- Environmental exposures such as radon and air pollution
- Occupational factors
Together, these account for one of the leading causes of cancer deaths worldwide.
Are Women More Vulnerable If They Don’t Smoke?
Research highlighted by the American Cancer Society suggests that women who have never smoked may be slightly more susceptible to lung cancer than men. Hormonal influences and genetic differences are thought to play a role.
How to Lower Your Risk
You can lower your risk of lung cancer by taking practical steps such as:
- Testing homes for radon
- Avoiding secondhand smoke
- Using protective equipment in hazardous workplaces
- Limiting exposure to polluted environments
- Prioritizing regular check-ups and early detection
Maintaining good lung health and seeking timely evaluation can significantly improve survival rates.
Diagnosis and Lung Cancer Treatment Options
Early diagnosis remains one of the most important factors in survival. Advances in screening and imaging have improved early detection for people at higher risk. Today’s treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, depending on cancer type and stage.
Finding the Best Doctor for Lung Cancer in Kolkata
Choosing the right specialist plays a major role in outcomes. Patients in Kolkata benefit from consulting an experienced lung cancer specialist in Kolkata such as Dr Sandip Ganguly, who is widely regarded as one of the best options for comprehensive lung cancer care, from diagnosis to advanced treatment planning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 90% of cancer caused by?
About 90% of cancers are linked to lifestyle and environmental factors such as smoking, pollution, infections, occupational exposure, and diet rather than inherited genes alone.
What causes stage 4 lung cancer in a non-smoker?
Late diagnosis, genetic mutations, radon exposure, air pollution, and occupational hazards are common reasons advanced lung cancer can develop in non-smokers.
What are the top 3 causes of lung cancer?
Smoking, environmental exposures like radon and air pollution, and genetic or workplace-related risks.
Are women more susceptible to lung cancer than men if they don’t smoke?
Evidence suggests women may have a slightly higher susceptibility due to hormonal and genetic influences, even without smoking.